Recognized By:





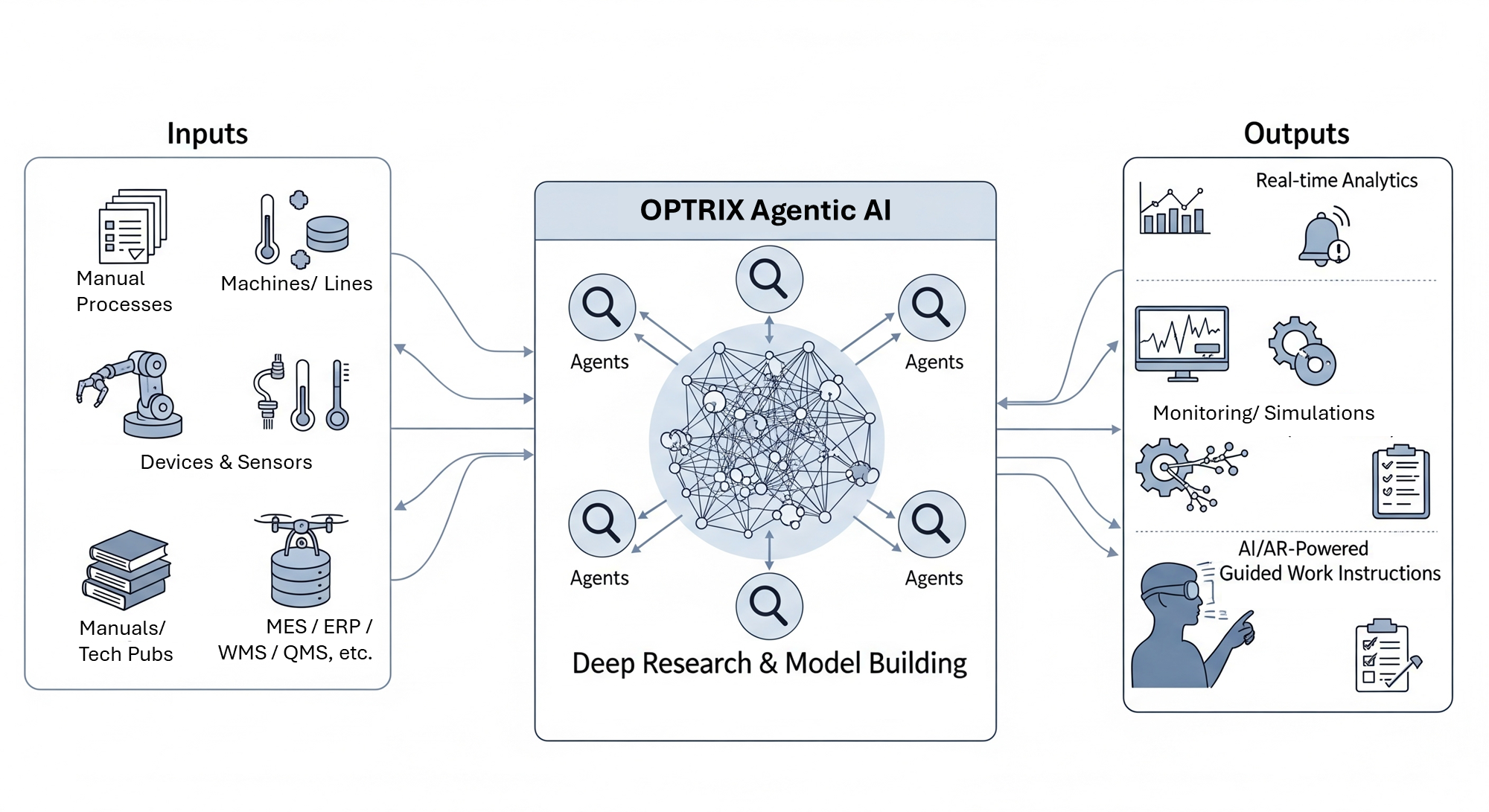
Intelligent Product Use Cases
Industry-specific solutions powered by OPTRIX AI & AR
Self-optimizing process intelligence that improves continuously
Industry: Manufacturing & Pharma
Capability: Adaptive workflows with continuous optimization
Outcome: Operations that achieve new performance levels automatically
AR-guided maintenance operations with AI-powered training systems
Industry: Defense & Manufacturing
Capability: Expert knowledge transfer through immersive AR training
Outcome: Operations that prevent problems and train workers simultaneously
Real-time guidance from experts anywhere, anytime eliminating delays and improving uptime
Industry: Agnostic
Capability: Immediate access to expert knowledge through real-time collaboration
Outcome: No delays, minimal downtime, and improved productivity
AR-powered railway inspection and maintenance systems
Industry: Transportation & Infrastructure
Capability: Real-time safety monitoring with AR-guided inspection
Outcome: Operations that maintain critical rail infrastructure intelligently
Operational ResultsReal Impact, Measurable Outcomes
Organizations transforming operations through intelligent systems